San Francisco is in crisis. The city that was once the pride of the West Coast has become a symbol of lawlessness, addiction, and failed leadership. London Breed’s policies, flip-flopping on key issues, have taken us to this point. Under her watch, San Francisco has experienced record-high overdose deaths, rampant open-air drug use, and an escalation of public disorder.
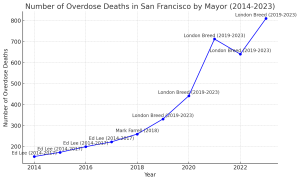
In 2023, San Francisco witnessed the deadliest year on record for overdose deaths. More than 3,000 lives have been lost to fentanyl during Breed’s tenure, and the city has spiraled into chaos. Yet, despite these catastrophic numbers, Mayor Breed continues to mislead San Franciscans with failed policies, political opportunism, and inconsistency.
As the 2024 mayoral election approaches, San Franciscans must ask themselves: Is this the future we want for our city?

Breed’s Flip-Flopping on Safe Consumption Sites: A Failed Experiment
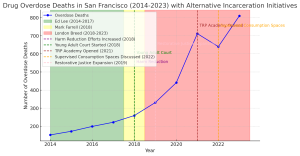
In 2020, Mayor Breed announced her plan to create safe consumption sites, where individuals could use drugs under supervision. Breed championed these sites as part of a broader “harm reduction” strategy to address the opioid crisis. But as overdose deaths skyrocketed, it became clear that these policies were not solving the problem. Instead, they were enabling it.
Breed’s support for the Tenderloin Linkage Center, a “state of emergency” experiment in the heart of San Francisco’s Tenderloin District, allowed drug users to openly consume narcotics under the guise of harm reduction. In just 11 months, the center reversed 333 overdoses, but rather than addressing the root cause of addiction or cleaning up the streets, the site became a symbol of Breed’s failure to get control of the crisis.
Breed’s response? Close the center without explanation in December 2022. Her experiment ended, leaving the city with nothing but higher death tolls and continued disorder. Instead of delivering solutions, Breed’s leadership amounted to little more than an expensive failed experiment.
Inconsistency at the Helm: Political Survival Over San Francisco’s Well-Being
Breed’s recent pivot to law-and-order rhetoric is nothing more than an attempt to salvage her political career as the 2024 mayoral election approaches. After years of enabling open-air drug use through her harm reduction policies, she has now begun increasing police patrols and arrests in a transparent effort to convince voters she’s serious about public safety.
This shift isn’t based on conviction or a real plan—it’s pure political calculation. Mayor Breed has seen the writing on the wall. She knows San Franciscans are fed up with the lawlessness, the crime, the rampant drug use, and the neglect of public safety. But after years of facilitating and perpetuating addiction, her sudden crackdown rings hollow.
Where was this concern for public safety when she allowed open drug use in the Tenderloin? Where was the law-and-order approach when she pushed for safe consumption sites while overdose deaths surged to record highs?
Breed’s actions show a clear pattern: she panders to public opinion only when it benefits her politically. In 2020 and 2021, it was politically expedient to push for harm reduction. Now, with an election looming, she’s flipped to a tougher stance on crime. But after years of enabling the very disorder she now claims to be addressing, can San Franciscans trust her sudden shift?
Safe Consumption Sites: Enabling Lawlessness, Perpetuating Addiction
Breed’s support for safe consumption sites has had devastating consequences. While these sites were supposed to reduce harm, they normalized drug use and contributed to the public disorder that now defines San Francisco’s streets. And the evidence is clear: under Breed’s leadership, overdose deaths soared.
Governor Gavin Newsom, recognizing the dangers posed by these sites, vetoed a state bill that would have allowed them to operate legally. Yet, even after this veto, Breed continued to push for local sites, defying state law and ignoring the public’s safety.
Her insistence on opening safe consumption sites, even when faced with overwhelming evidence that they were failing, shows a clear disregard for the well-being of San Francisco’s residents. Instead of providing treatment and recovery options, these sites acted as enablers of addiction, keeping people trapped in a cycle of drug use and dependence.
San Francisco needs leadership that prioritizes recovery, safety, and accountability. Mayor Breed’s harm reduction strategy has failed. Her inconsistency and opportunism have created an environment where addiction flourishes, crime rises, and families feel unsafe.
Mark Farrell: The Leader San Francisco Needs
In contrast to Breed’s failed leadership, Mark Farrell has a clear, consistent, and actionable plan to fix San Francisco. He understands that law and order are essential to rebuilding the city, but he also knows that addiction must be treated with a recovery-first approach.
Farrell’s plan focuses on:
- Declaring a fentanyl state of emergency, with more armed California National Guard officers to address open-air drug markets and trafficking.
- Building a large-scale, 24/7 centralized intake center, staffed with social workers and medical professionals, to triage those in need and guide them through recovery.
- Scrapping Breed’s failed Overdose Prevention Plan, which has enabled drug use, and shifting the focus to recovery-first and abstinence-based options.
- Increasing police staffing levels to serve as a deterrent to drug dealing and public drug use, while also providing more recovery beds and detox opportunities for those in need.
- Reforming pretrial detention to end the cycle of catch-and-release policies that Breed allowed to flourish, and ensuring that individuals revived with Narcan receive mandated treatment.
Mark Farrell’s vision is one of a cleaner, safer, and thriving San Francisco—a city where families can walk the streets without fear, where businesses can prosper, and where addiction is treated as a public health crisis with real solutions, not empty promises.
Time to Choose: Failed Leadership or Real Change?
San Franciscans deserve better than London Breed’s inconsistency and political gamesmanship. Under her watch, our city has fallen into chaos. Her policies have facilitated addiction, enabled lawlessness, and contributed to the deterioration of public safety.
Mark Farrell offers the real leadership San Francisco needs. He has a plan to save lives, restore safety, and clean up our streets. This election is a choice between more of the same chaos under Breed or a better, brighter future for San Francisco with Farrell at the helm.
The choice is yours. Vote for Mark Farrell. It’s time to fix San Francisco.
“Paid for by the San Francisco Deputy Sheriffs’ Association PAC. Not authorized by a candidate or committee controlled by a candidate. Financial disclosures are available at sfethics.org.”






 Today, September 9th, 2024, marks a pivotal moment for the San Francisco Sheriff’s Office. President Ken Lomba met with Sheriff Miyamoto to address two critical issues impacting our staffing and recruitment efforts: reforming the testing process and implementing second-step pay for new applicants.
Today, September 9th, 2024, marks a pivotal moment for the San Francisco Sheriff’s Office. President Ken Lomba met with Sheriff Miyamoto to address two critical issues impacting our staffing and recruitment efforts: reforming the testing process and implementing second-step pay for new applicants. In the competitive landscape of law enforcement, the ability to attract and retain qualified personnel is not just a goal—it’s a necessity. For the San Francisco Sheriff’s Office (SFSO), however, this has become an area of significant failure. The challenges we face are not solely due to external factors or the inherent difficulties of law enforcement recruitment. Instead, much of the problem lies within the SFSO itself, particularly due to the lack of decisive action and strategic use of available resources by its leadership.
In the competitive landscape of law enforcement, the ability to attract and retain qualified personnel is not just a goal—it’s a necessity. For the San Francisco Sheriff’s Office (SFSO), however, this has become an area of significant failure. The challenges we face are not solely due to external factors or the inherent difficulties of law enforcement recruitment. Instead, much of the problem lies within the SFSO itself, particularly due to the lack of decisive action and strategic use of available resources by its leadership.